Stoichiometry synthesis of calcium carbonate is a fascinating chemical process that holds immense significance in various industries. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate details of this synthesis, exploring its fundamental principles, practical applications, and economic implications.
The stoichiometric synthesis of calcium carbonate involves a carefully controlled reaction between calcium hydroxide and carbon dioxide, resulting in the formation of calcium carbonate. This process is governed by specific conditions, including temperature, concentration, and the availability of reactants. Understanding the stoichiometry of this reaction is crucial for optimizing the synthesis and achieving desired outcomes.
Stoichiometry and Chemical Reactions
Stoichiometry is the study of the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in chemical reactions. It allows us to predict the amounts of reactants and products involved in a given reaction.
A balanced chemical equation represents a chemical reaction in which the number of atoms of each element on the reactants’ side of the equation equals the number of atoms of that element on the products’ side. Coefficients in front of chemical formulas in a balanced equation indicate the relative amounts of reactants and products involved.
Synthesis of Calcium Carbonate, Stoichiometry synthesis of calcium carbonate
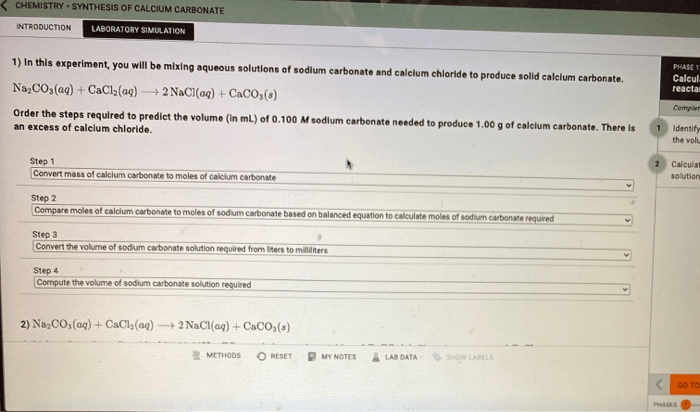
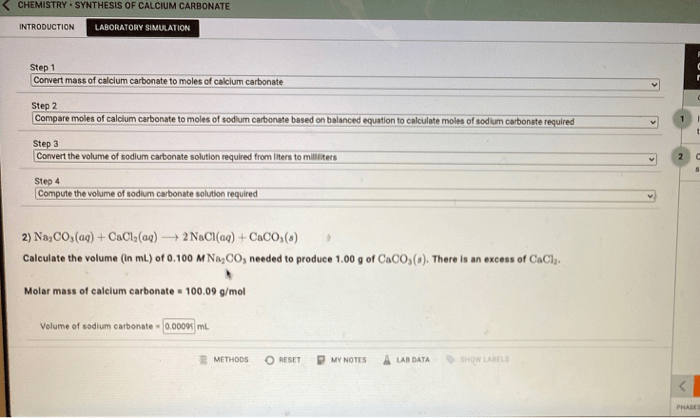
Calcium carbonate (CaCO 3) can be synthesized through the reaction of calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH) 2) and carbon dioxide (CO 2):
Ca(OH)2+ CO 2→ CaCO 3+ H 2O
Calcium hydroxide provides the calcium ions (Ca 2+), while carbon dioxide provides the carbonate ions (CO 32-). The reaction occurs in aqueous solution and requires specific conditions, such as temperature and concentration, to facilitate the formation of calcium carbonate crystals.
Methods for Synthesizing Calcium Carbonate
Precipitation Method:
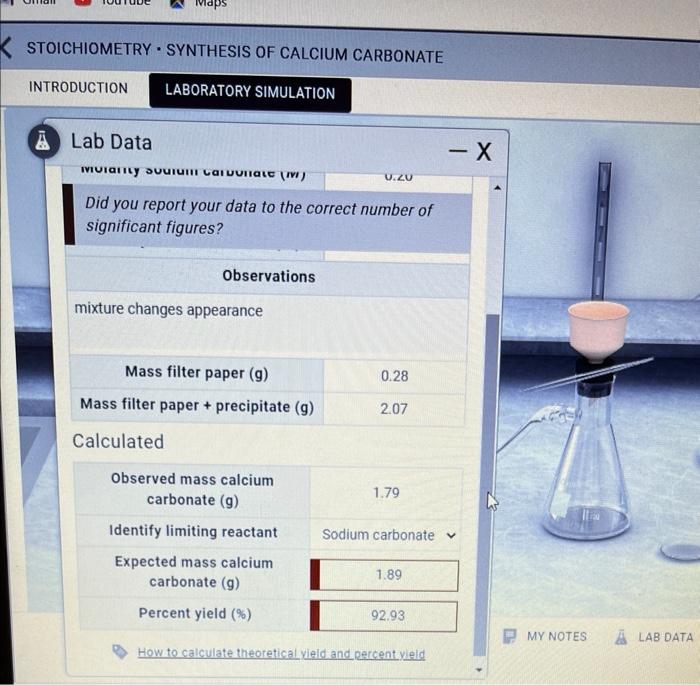
The precipitation method involves mixing solutions of calcium hydroxide and sodium carbonate (Na 2CO 3) to form an insoluble precipitate of calcium carbonate. Temperature and concentration play crucial roles in controlling the size and morphology of the precipitated crystals.
- Advantages: Simple and inexpensive, produces high-purity calcium carbonate.
- Disadvantages: Requires precise control of conditions, can be time-consuming.
Applications of Calcium Carbonate
- Construction:As a raw material for cement, mortar, and other building materials.
- Papermaking:As a filler and coating agent to improve paper quality.
- Pharmaceuticals:As an antacid, calcium supplement, and drug carrier.
- Cosmetics:As a filler and opacifier in powders and creams.
- Agriculture:As a soil amendment to neutralize acidity and provide calcium for plant growth.
Calcium carbonate has significant economic importance due to its wide range of applications in various industries.
Commonly Asked Questions: Stoichiometry Synthesis Of Calcium Carbonate
What is the significance of stoichiometry in calcium carbonate synthesis?
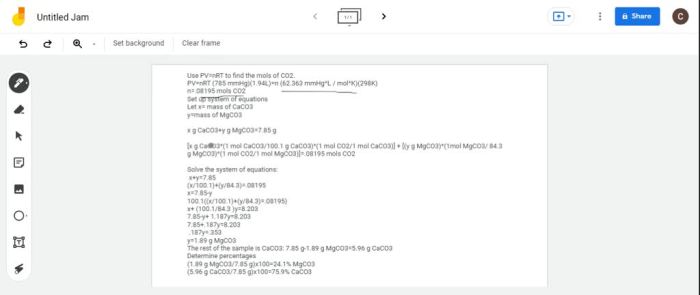
Stoichiometry plays a vital role in calcium carbonate synthesis, as it determines the precise proportions of reactants required for complete conversion. By adhering to stoichiometric ratios, the reaction can be optimized to maximize yield and minimize waste.
How does temperature influence the precipitation method for calcium carbonate synthesis?
Temperature is a critical factor in the precipitation method, as it affects the solubility and reaction kinetics. Higher temperatures generally favor the formation of larger and purer calcium carbonate crystals, while lower temperatures may lead to smaller and less crystalline products.
What are the advantages of using the precipitation method for calcium carbonate synthesis?
The precipitation method offers several advantages, including simplicity, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. It is widely used in industrial settings due to its ability to produce large quantities of calcium carbonate with controlled properties.