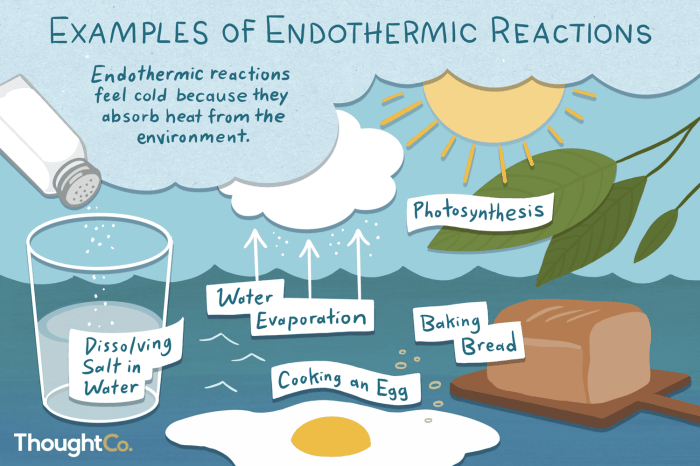
Classify each process as an endothermic or exothermic process. Endothermic and exothermic processes are two fundamental types of chemical reactions that involve energy transfer. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the differences between these processes, provide examples, and discuss their applications and factors affecting their rates.
Processes and Their Classifications: Classify Each Process As An Endothermic Or Exothermic Process
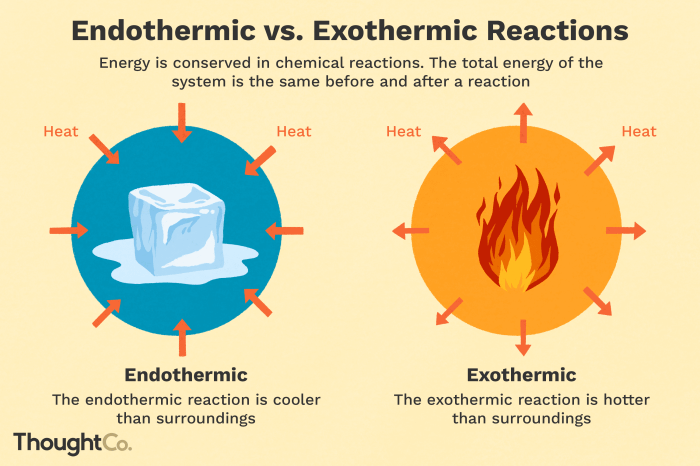
Processes can be classified as either endothermic or exothermic based on their energy exchange with the surroundings.
Endothermic processesabsorb energy from the surroundings, resulting in an increase in internal energy. This energy is stored within the system, leading to a decrease in temperature.
Exothermic processes, on the other hand, release energy to the surroundings, resulting in a decrease in internal energy. This energy is transferred to the surroundings, leading to an increase in temperature.
Identifying Endothermic and Exothermic Processes
To identify an endothermic process, look for a decrease in temperature as the process occurs. This indicates that energy is being absorbed from the surroundings.
Conversely, to identify an exothermic process, look for an increase in temperature as the process occurs. This indicates that energy is being released to the surroundings.
The following table summarizes the characteristics of endothermic and exothermic processes:
| Process | Energy Change | Temperature Change | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Melting of ice | Endothermic | Increase | Endothermic |
| Burning of wood | Exothermic | Decrease | Exothermic |
| Dissolving salt in water | Endothermic | Increase | Endothermic |
| Neutralization of acid and base | Exothermic | Decrease | Exothermic |
| Condensation of water vapor | Exothermic | Increase | Exothermic |
Applications of Endothermic and Exothermic Processes
Endothermic processesare used in various applications, including:
- Cooling systems, such as air conditioners and refrigerators
- Melting ice and snow
- Cooking and baking
- Chemical reactions that require energy input
Exothermic processeshave industrial applications, such as:
- Welding and cutting metals
- Generating heat in furnaces and boilers
- Propelling rockets and jet engines
- Manufacturing cement and glass
Factors Affecting the Rate of Endothermic and Exothermic Processes, Classify each process as an endothermic or exothermic process
The rate of endothermic processes is influenced by factors such as:
- Surface area of the reactants
- Temperature
- Concentration of the reactants
- Presence of a catalyst
The rate of exothermic processes is influenced by factors such as:
- Surface area of the reactants
- Temperature
- Concentration of the reactants
- Presence of an inhibitor
FAQ Summary
What is the key difference between endothermic and exothermic processes?
Endothermic processes absorb energy from the surroundings, causing a decrease in temperature, while exothermic processes release energy into the surroundings, leading to an increase in temperature.
Provide an example of an endothermic process.
Melting of ice is an endothermic process as it requires energy to break the intermolecular bonds holding the water molecules in a solid state.
How do factors like surface area and temperature influence the rate of exothermic processes?
Increasing surface area allows for more reactant molecules to interact, accelerating the exothermic process. Higher temperatures provide more energy, increasing the frequency of collisions between reactant molecules, thereby enhancing the reaction rate.